The human vocal range is often described in extreme, almost mythical terms: five octaves, impossibly high notes, incredibly deep lows. When I first encountered those claims, I assumed my own voice was limited—or that I was missing some hidden potential.
The human vocal range typically spans about 2 octaves for most people, while trained singers often reach 3–4 octaves. It varies by voice type, age, gender, and training, with extreme ranges exceeding 5 octaves in rare cases.
What Is the Human Vocal Range?
The human vocal range is the span of pitches a person can sing, typically about 1.5–2 octaves for most people and 3–4 octaves for trained singers. It varies by voice type, age, gender, and training, with rare cases exceeding 5 octaves.
The human vocal range refers to the complete span of pitches the human voice is physically capable of producing, from the lowest to the highest sounds, across all vocal registers and techniques.
This includes extreme and specialized vocal sounds, not just notes used in everyday singing.
How Wide Is the Human Vocal Range?
When measured across all registers, the human voice can exceed 5 octaves in very rare cases.
However, this number is often misunderstood.
Important distinction
- Human vocal range → biological limits
- Singing range → usable, musical notes
Most people never sing at the biological extremes—and don’t need to.
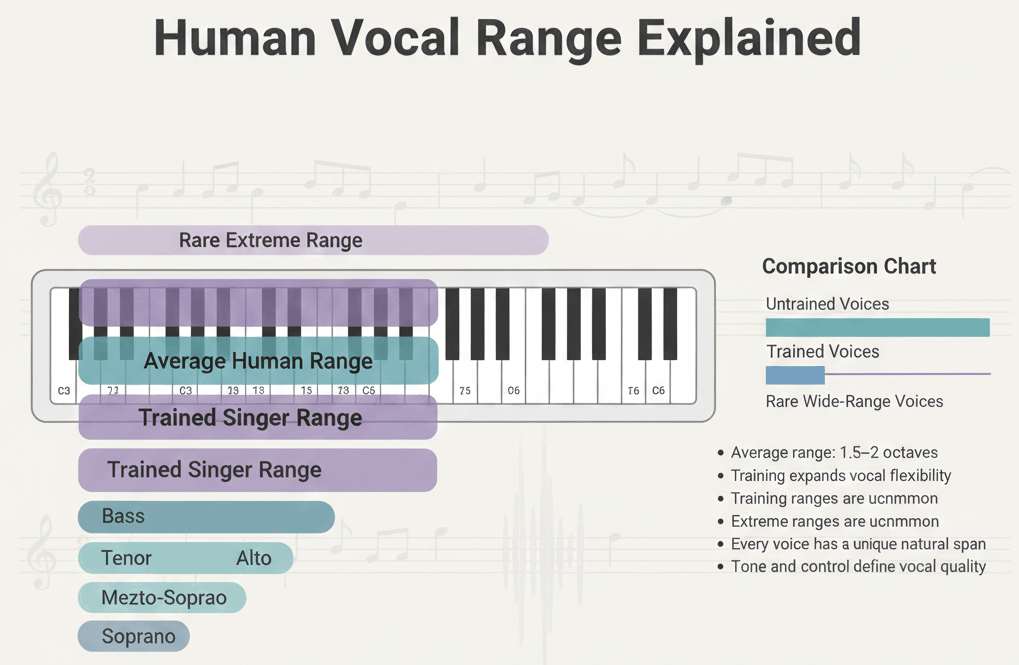
Average Human Vocal Range (What’s Normal)
Most people, trained or untrained, use:
- About 2 to 3 octaves comfortably
This aligns with data summarized in average vocal range.
That range is more than enough for:
- expressive singing
- professional performance
- long-term vocal health
A larger range does not automatically mean better singing.
Lowest and Highest Human Vocal Sounds
Lowest Human Vocal Sounds
- Produced using subharmonics or fry-based techniques
- Can fall below E2
- Rarely used musically
Highest Human Vocal Sounds
- Produced using the whistle register
- Can exceed C6 in rare cases
- Highly specialized and optional
These sounds expand the human vocal range, but not the average singing range.
Vocal Registers and Why They Matter
The human vocal range exists because of different vocal registers, each produced differently by the vocal folds.
| Register | What It’s Used For |
|---|---|
| Chest voice | Speech & lower singing |
| Head voice | Higher melodic singing |
| Whistle register | Extreme high sounds |
| Subharmonics | Extreme low effects |
Understanding registers explains why humans can make extreme sounds—but usually don’t sing there.
Human Vocal Range vs Singing Range vs Tessitura
This distinction cleared up most of my confusion.
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Human vocal range | All possible vocal sounds |
| Singing range | Controlled, musical notes |
| Tessitura | Where the voice works best |
Charts showing extreme ranges often skip this explanation. For a visual reference, see vocal range chart.
How Many Octaves Can Humans Sing?
A realistic breakdown:
- Most people: 2–3 octaves
- Well-trained singers: 3–4 octaves
- Rare outliers: 5+ octaves (specialized techniques)
For octave-specific context, see how many octaves and the detailed breakdowns for 3-octave vocal range, 4-octave vocal range, and 5-octave vocal range.
Should You Try to Reach the Full Human Vocal Range?
Short answer: No.
Chasing the biological limits of the human voice often:
- increases strain
- reduces consistency
- slows real progress
How to Understand Your Own Voice (Practically)
Instead of comparing yourself to extremes:
- Measure your comfortable vocal range
- Track consistency across days
- Identify where fatigue appears
- Monitor pitch stability
Vocal Health and the Human Vocal Range
Most vocal problems come from pushing beyond usable range—not from lacking range.
Protect your voice by reviewing:
A wider range is meaningless if it isn’t sustainable.
Common Myths About the Human Vocal Range
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| “Humans naturally sing 5 octaves” | Most don’t |
| “Wide range = better singer” | Control matters more |
| “Extreme notes are goals” | They’re optional |
| “Range equals skill” | Technique matters more |
The human vocal range:
- can exceed 5 octaves in rare cases
- includes extreme, non-musical sounds
- is much wider than normal singing range
- does not define singing ability
Find your vocal range instantly at https://vocalrangetester.com/.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the full human vocal range?
Across all registers, the human voice can exceed 5 octaves in rare cases.
2. What is the average human vocal range?
Most people use about 2–3 octaves comfortably.
3. What is the lowest note a human can produce?
Some can produce sounds below E2 using specialized techniques.
4. What is the highest note a human can sing?
Whistle register notes can exceed C6 in rare cases.
5. Do trained singers have wider ranges?
Often yes, but control matters more than size.
6. Is a wide vocal range necessary?
No. Musicality and consistency matter more.
7. Does vocal range change with age?
Yes. Range and tessitura can shift over time.